Network Latency Demystified: Causes and Practical Solutions to Reduce It
Network latency is often an overlooked aspect of digital communication. Despite streaming videos, transacting financially, using cloud applications or participating in video calls, excessive latency can significantly impact performance.
By having a clear picture of the causes of network latency and implementing effective solutions, both businesses and individuals can optimize their networks for faster and more reliable performance. Here are some of the main causes of network latency and how we could minimize it.
Network Latency

Network latency is the time data takes to travel from its source to its destination and back. It is typically measured in milliseconds, and lower latency translates to better network performance. For example, in cloud computing, a latency of less than 20 milliseconds is considered optimal for real-time applications such as video conferencing or interactive services. Latencies above 50 milliseconds can result in noticeable delays, affecting the user experience, especially in critical operations like financial transactions or live data processing.
Physical distance, network congestion, hardware constraints and ineffective routing are some of the variables that affect network delay. Let’s take a closer look at these reasons.
Common Causes of Network Latency
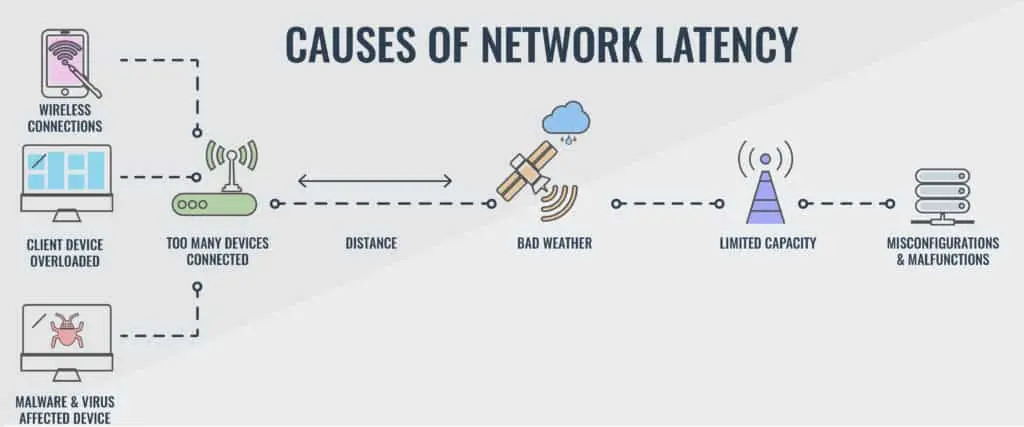
Credit: TezHost
1. Physical Distance
The farther data must travel, the longer it takes to reach its destination. If a user in Kisumu is accessing a server in Mombasa, data packets must cross thousands of miles, traveling through multiple networks and switches, which increases latency.
Solution:
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to store cached versions of content closer to users.
- Select servers located geographically near the target audience to minimize travel distance.
2. Network Congestion
When too many devices are trying to send and receive data simultaneously, it creates congestion, slowing down network speeds. This is common in public Wi-Fi networks, corporate offices and cloud service providers during peak hours.
Solution:
- Implement Quality of Service (QoS) policies to prioritize critical applications like video conferencing and VoIP over less urgent traffic.
- Upgrade bandwidth or switch to a dedicated internet connection.
3. Routing Inefficiencies
Data packets travel through multiple routers before reaching their destination. If the routing protocols used are outdated or inefficient, packets may take unnecessarily long paths, increasing latency.
Solution:
- Optimize routing by configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for efficient path selection.
- Work with an ISP that offers optimized global routing.
4. Hardware Limitations
Older networking equipment, including routers, switches and firewalls, can bottleneck performance, leading to increased latency.
Solution:
- Upgrade network infrastructure with modern, high-speed routers and switches.
- Use cloud-based acceleration and network optimization services.
5. Transmission Medium
Different types of transmission mediums affect latency. Fiber optic cables offer lower latency than traditional copper cables, while wireless networks experience higher latency due to interference.
Solution:
- Choose fiber optic connections over copper where possible.
- Minimize reliance on Wi-Fi and opt for wired Ethernet connections.
- Ask your local cloud service provider to provide you with local bandwidth using fiber connectivity.
6. DNS Resolution Delays
A slow Domain Name System (DNS) can delay the time it takes to translate a domain name into an IP address.
Solution:
- Use fast, reliable DNS providers like Google DNS (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1).
- Set up local DNS caching to reduce lookup times.
- Collaborate with your local cloud service provider to implement faster DNS name resolution services.
Summary: Practical Solutions to Reduce Network Latency
Reducing network latency requires a combination of cloud services, network optimization techniques, and best practices. Here are some key strategies:
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs reduce latency by caching content at multiple locations worldwide, ensuring users can access data from the nearest server rather than a distant origin.
- Implement Edge Computing: Edge computing processes data closer to the source instead of sending it to a centralized data center, significantly reducing latency for IoT applications and real-time analytics.
- Optimize TCP/IP Settings: Tweaking Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) settings, such as adjusting the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) and Receive Window Size (RWIN), can help optimize network performance.
- Leverage Angani’s Cloud Services: Working with Angani, you can upgrade to a higher-bandwidth, lower-latency internet service plan or use dedicated business internet connections to dramatically improve latency.
- Reduce Network Hops: Minimizing the number of routers and network devices that data passes through before reaching its destination can significantly reduce latency.
- Enable Quality of Service (QoS): QoS settings allow network administrators to prioritize latency-sensitive applications like VoIP, financial transactions, and video streaming over lower-priority traffic.
- Use Low-Latency Protocols: For applications like real-time communication and stock trading, using low-latency protocols such as WebRTC, QUIC and UDP instead of traditional TCP can improve performance.
- Perform Regular Network Monitoring: Monitoring tools such as Wireshark, SolarWinds and PRTG help diagnose latency issues by analyzing packet loss, jitter and response times.
- Minimize Wi-Fi Interference: Wi-Fi signals can experience interference from physical obstacles, electronic devices and neighboring networks. Using 5 GHz Wi-Fi, placing routers in open areas and reducing obstructions can help improve signal quality.
Partnering with Angani for cloud solutions and network optimization services can help your business achieve faster and more reliable network performance.
Real-World Applications of Low-Latency Networks
1. Financial Trading
The financial industry depends on low-latency networks for high-frequency trading (HFT), where milliseconds can mean the difference between profit and loss. Trading platforms use low-latency algorithms to execute trades instantly, ensuring traders can respond to market changes in real-time.
How Low Latency Helps:
- Enables faster trade execution, reducing the risk of slippage.
- Provides a competitive advantage in algorithmic trading.
- Ensures accurate and real-time stock price tracking.
2. Telemedicine
Telemedicine applications, including remote surgeries and video consultations, require real-time data transmission with minimal latency. In robot-assisted surgeries, doctors control robotic arms remotely, requiring immediate feedback for precise movements.
How Low Latency Helps:
- Ensures accurate, real-time video and audio communication.
- Allows for seamless operation of remote medical devices.
- Enhances patient care through real-time diagnostic data transmission.
3. Cloud-Based Applications
Businesses rely on cloud-based platforms like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365 and Slack for collaboration. High latency in these applications can lead to slow file synchronization, delayed notifications, and poor video conferencing quality.
How Low Latency Helps:
- Speeds up file uploads and downloads.
- Reduces delays in video calls and remote meetings.
- Enhances collaboration by ensuring real-time document editing and sharing.
4. Live Streaming and Video Conferencing
Streaming services like Netflix, YouTube, and Twitch and video conferencing platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams require minimal latency to deliver smooth, high-quality video experiences.
How Low Latency Helps:
- Prevents buffering and lag in video streams.
- Ensures real-time communication during video calls.
- Improves user experience by delivering seamless content.
Final Thoughts

Network latency is a critical factor affecting digital experiences, streaming and cloud computing to financial transactions. By understanding its causes and implementing targeted solutions, businesses and individuals can significantly improve network performance.
Partner with us, East Africa’s best cloud services provider, to achieve these goals.
We offer cloud infrastructure, backup, disaster recovery, media streaming, cloud PABX and data analytics services, with local support and low latency. Enhance your digital environment by leveraging our expertise for superior network performance and reliability.

